Genome Block Store
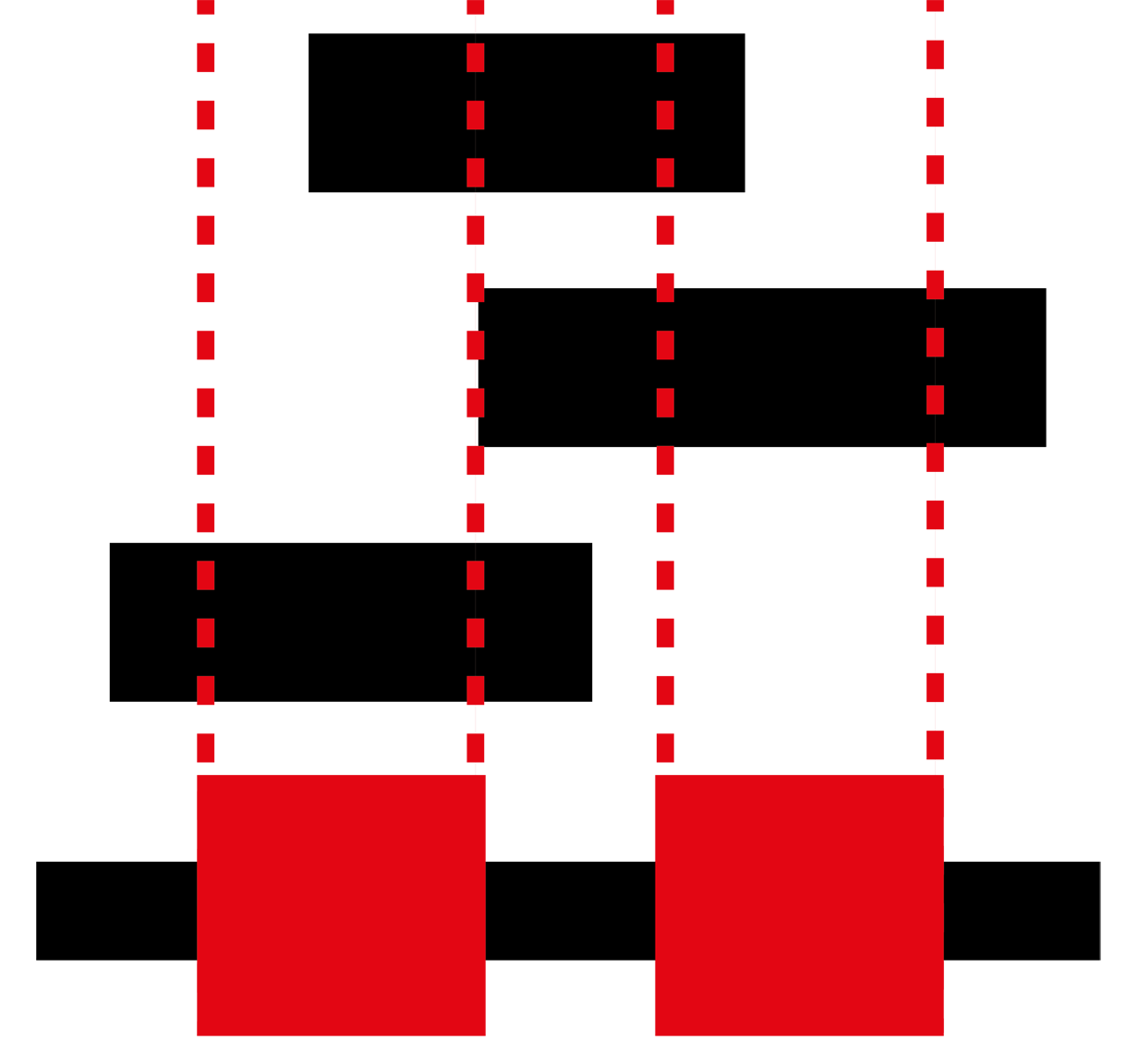
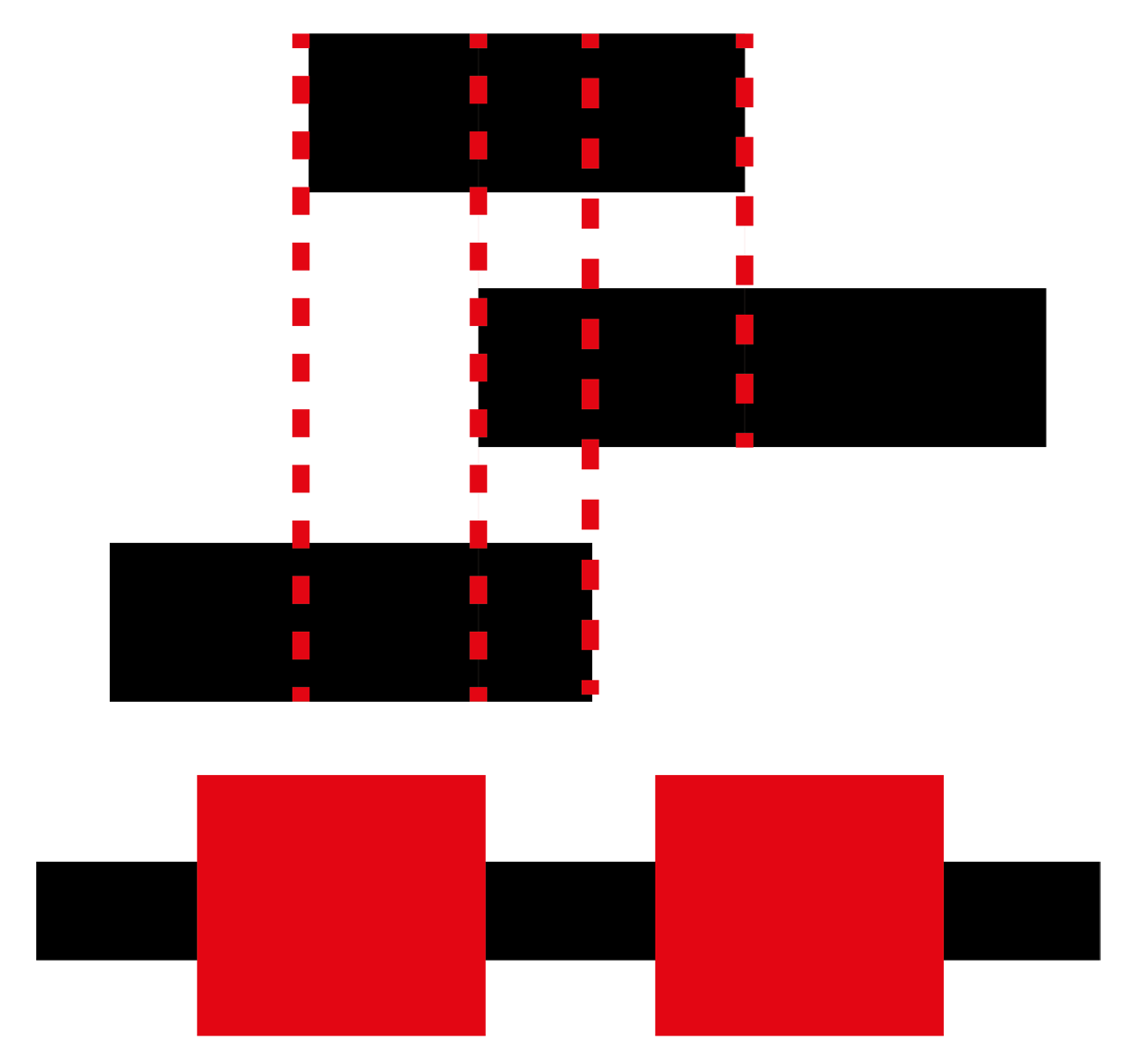
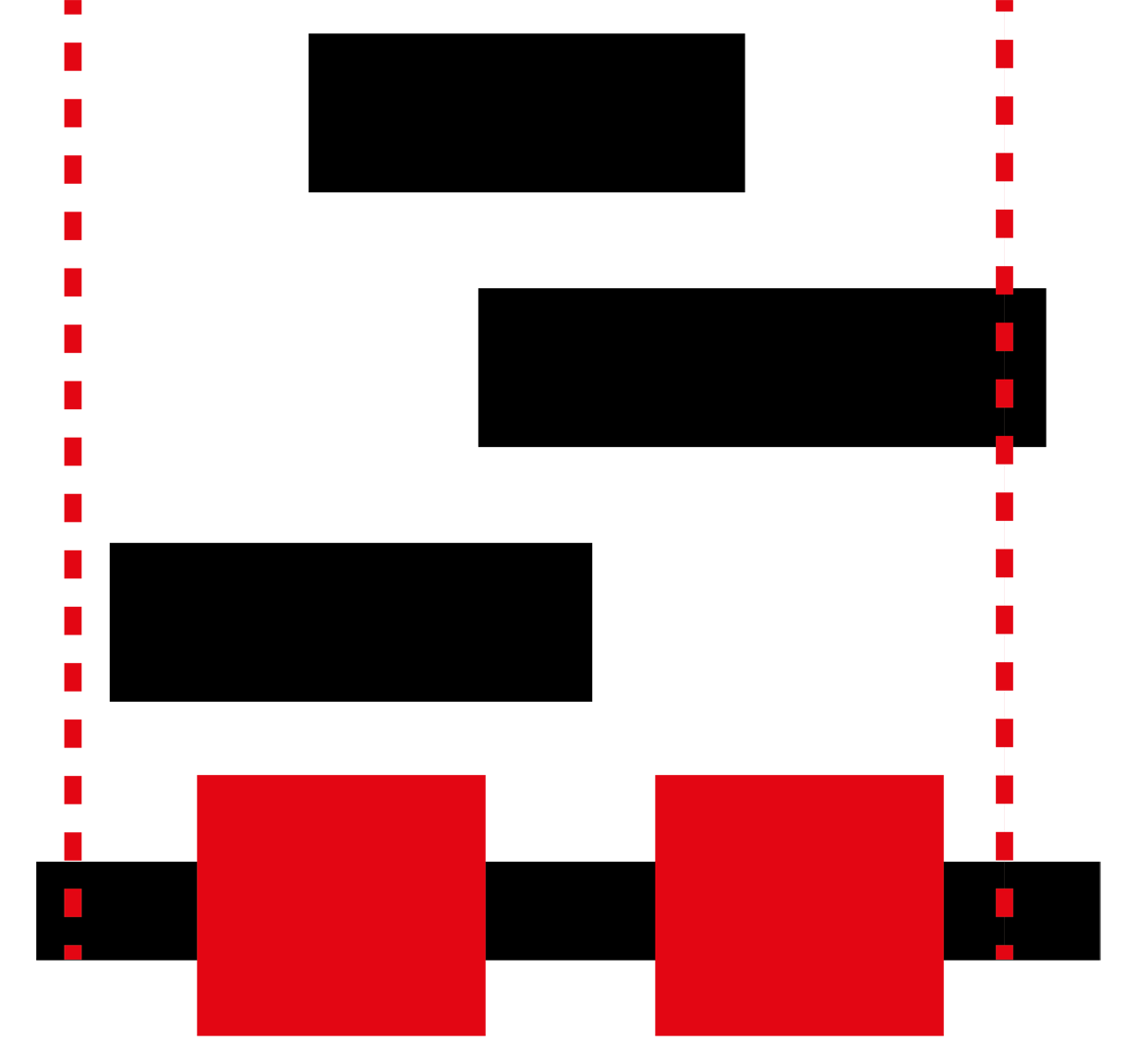
The GBS is a database of annotated genomic blocks produced from any software for any type of medium/large genomic event. Genomic blocks consist of start and end coordinates within a genome and are typically generated when inferring copy number variations, structural variations, losses of heterozygosity and linkage.
Precisely and rapidly interrogate the GBS
Three ways to search let you identify the events that are important to you
Gene List(s)
The GBS allows you to determine whether your candidate list of genes has been affected by any large-scale genomic events. These events have been shown to have massive functional roles in disease so rapid interrogation is key to rapid diagnosis.
Overlapping Blocks
Overlapping genomic blocks can be the product of agreement between different tools for calling genomic blocks within a single individual, or they can be overlapping between different individuals for the same or different methods.
Genomic Coordinates
Searching for all blocks within a specific set of genomic coordinates allows you to determine all important blocks in your area of interest. Many conditions are closely tied with a specific genomic location so being able to narrow your search greatly increases the chance of finding your answer rapidly.
Passive query
Query the GBS without even knowing you are
Storing genome blocks in the GBS enables rapid integration of genomic block information with short nucleotide variants in Seave. If a short variant in a sample is within a genomic block stored in the GBS for that sample, the GBS hit is displayed along with the rest of the annotation for the variant allowing an unparalleled integration of genomic information.